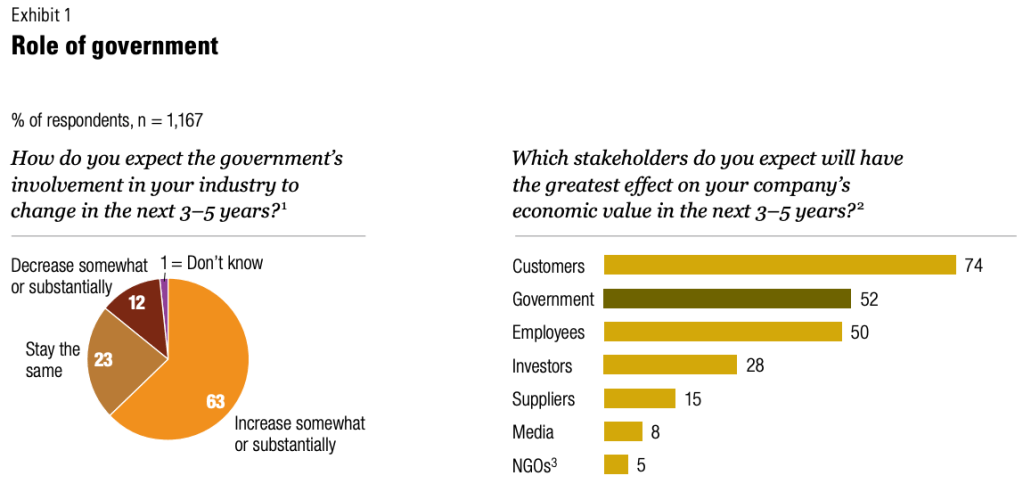
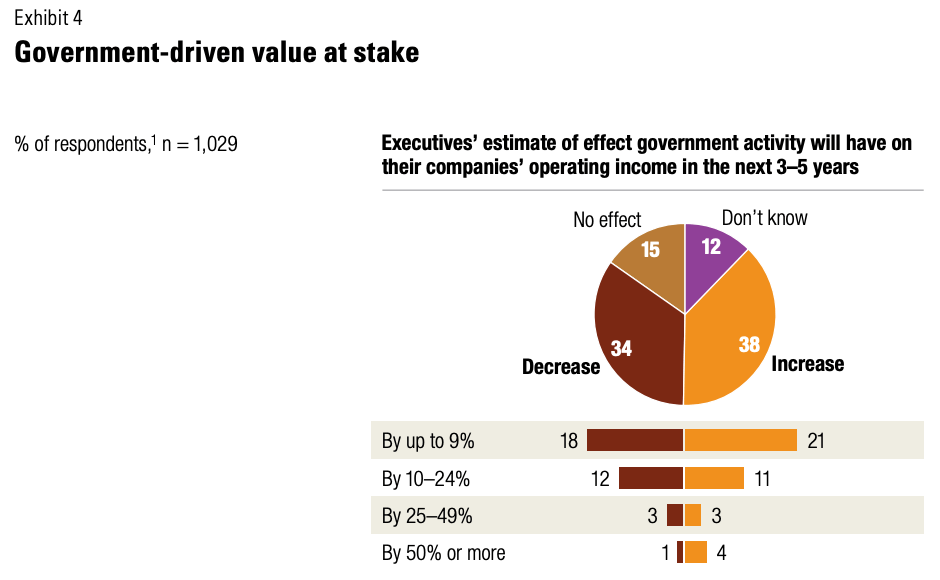
This white paper was a collaboration between myself, as primary writer and researcher, and Matt Stitt and Mike Nadol as editors and contributors. It was created as part of PFM’s work in the Bloomberg Results for America City Budgeting for Equity and Recovery program in 2021. The fully designed PDF can be viewed here.
Why This Matters?
Capital budgets and improvement plans present exceptional opportunities for governments to drive equitable outcomes in municipalities, particularly when budgeting for recovery. The significant spending power authorized through capital budgets – multiple billions for some jurisdictions – can allow for increased, targeted spending on geographies that historically lacked investment from the public and private sectors. In addition, the job creation necessary to complete these projects offer workforce and economic development opportunities for residents and businesses. Because the Capital Improvement Plan (CIP) typically requires a multi-year plan and planning process, it provides a framework that can be adapted to equitable purposes rather than created from scratch. When taken together with the scale of funding available, the CIP presents a ready-made strategy for planning, implementing, and evaluating projects that achieve enduring equitable outcomes.
Introduction
Infrastructure is the fabric that enables community connection, economic opportunity, and civic life in the United States. Eighty percent of public spending on these vital projects (from roads and bridges to parks and recreation centers) is provided by state and local governments. Yet despite its importance to everything from commerce to public health, the national total deferred maintenance on infrastructure assets could be as high as $1 trillion.[1]
Additionally, most cities have no structured mechanisms to incorporate equity considerations into their capital investment planning. Equity-based approaches to funding, project selection, and community input are still evolving and imperfect at best – but such approaches are now developing rapidly for operating budget allocations. To next integrate equity into longer-term financial strategies, Finance Directors, City Managers, and senior Elected Officials must all double-down on their efforts, sharpening their focus on capital investment planning. While there is no single solution that works for most cities – when it comes to matters of equitable impact, the best option is one that is place-based and reflective of the needs of a specific community. Ultimately, the process for equitable capital budgeting must be developed collaboratively and implemented through a thoughtful change management strategy.
This resource outlines a few strategies and case examples (related to equity in capital planning), from across the country, that can be adapted to the local context.
Using Capital Improvement Planning (CIP) Process to Drive Equitable Outcomes
To approach the CIP process in a manner that creates consistent, measurable, equity-focused results, PFM recommends first mapping the current process being used (including a timeline for key milestones) and bucketing the tasks into phases. Each of the following examples can be considered as a potential improvement to one key phase (i.e., swapping a current practice for a new tactic) or as part of a more comprehensive effort across the full process. Depending on local readiness, needs, and priorities, government staff can choose an approach that is politically feasible while building toward maximized impact.
Prioritize Projects that Align with Long-Term Strategic Goals
The Government Finance Officers Association identifies “identifying, tracking, and communicating” performance measures in budgeting, including the capital budget, to be a financial best practice.[2] To make such performance measures most impactful, city staff must align these metrics to the overall goals set by city leadership. In the City of Seattle, WA, for example, equity goals have been set by the Seattle 2035 comprehensive plan – and the City’s scorecard for capital investments uses detailed, quantifiable criteria to rank projects in terms of alignment with these goals.[3] Projects that score high on these measures (and, thus, are highly aligned to the plan) receive higher priority for funding than those with relatively lower scores.
Develop a More Impactful Community Benefit Agreement Structure
If well-designed, Community Benefits Agreements (CBAs) centered on equity issues can be extremely impactful for cities. In Sacramento, CA, for example, a recent CBA developed for a multi-billion-dollar mixed use development generated $50 million in funding for affordable housing, anti-displacement investment, prioritized hiring for residents, and improved public transit infrastructure. These benefits were developed, prioritized, and supported by direct resident input. The evaluation firm highlighted dialogue with community members (versus presentations) – designing projects that not only increase revenues, but also deliver non-monetary benefits to residents and businesses. The firm also recommended reevaluating success measures (i.e., rethinking straight, or traditional, financial return-on-investment).[4]
Formalize “% for X” Investment Goals in Major Capital Projects
The strength of the capital budget and plan as a tool to promote equity is that its spending power, especially when viewed over a multi-year time horizon, can dwarf the operating budget of a municipality. With this scale in mind, cities should consider a formal set-aside of X% in major capital projects (e.g., all projects with budgets over $2 million) – for the sole purpose of funding an equitable priority project. As an example, the City of Austin, TX, recently dedicated $300 million of a +$7 billion transit expansion program to affordable housing and anti-displacement programs for near neighbors.[5] Not only does this provide funding for an equitable priority, but also enhances the value of the transit assets themselves through potential increases in ridership.
Connect Capital Budgets and Workforce Development
All cities seek a robust, skilled workforce and a strong local economy – however, oftentimes workforce development funding is tied to imminent or even pre-existing job opportunities. By taking advantage of capital investments to drive small business growth and the development of local supply chains, municipalities that design creative programs (or partnerships) can generate a positive feedback loop of a stronger labor market, growing local firms, and increased quality and efficiency of capital projects. For example, one city in the current Bloomberg Philanthropies/What Works Cities City Budgeting for Equity and Recovery cohort is working to design a sidewalk maintenance program that would include a set amount of work conducted each year by apprentices and workers seeking employment. This helps to improve walkability and economic activity, while also training residents to work in trades that offer family-sustaining wages and add value to businesses in the City.
Seek Strategies for Co-Investment
State and federal funding can be a source of “fuel” for capital project development. Enterprising city staff can apply for grants that award funding for not-as-obvious capital investments that expand program capacity, and, in the best-case scenario, generate a return to both the city and its residents. The Philadelphia Energy Authority’s Solar Savings Grant Program, for example, leverages funding from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania for green energy projects to offset the cost of installing solar panels on low- and moderate-income households’ roofs.[6] The grants lower the overall costs of the program, residents save money on their electric bills each month, and the city decreases its overall carbon footprint.
Set a Future-Focused Investment Strategy
An additional way to better leverage capital budget dollars is to invest in growing service areas based on demographic trends, and strategies that can reallocate funding to more equitable priorities. For example, there are mobile crisis teams operating in at least 25 cities across the country, and many more around the world. In Eugene, OR, the CAHOOTS program, a pioneer in this space, cost approximately $2 million to operate (in 2019), and is estimated to have saved approximately $23 million in public safety and public health costs.[7] While models for service delivery vary depending on the local context, cities that choose to develop this capacity internally can leverage capital investment to establish facilities, and potentially to procure first-response vehicles and other durable goods, that contribute to the treatment process. With such support, mobile crisis programs have the ability to lower the needed capacity in public safety (e.g., police and/or EMS/EMT first responders) and public health (e.g., hospital beds and social worker FTEs) over time. Investments like these also create an equitable outcome of clinically appropriate care delivered to residents in need (i.e., instead of holding residents in prison or police custody without timely treatment) while diverting from corrections populations and overburdened emergency rooms.
Callout Features – Case Studies
Redefining Return on Investment (ROI) through an Equity Lens
Moving towards equitable formulas for funding CIPs will naturally raise questions regarding ROI (i.e., will projects generate a financial return). Evaluation is a critical component of all capital investments, and these examples provide a clear guide.
- In Harris County, TX, officials recently moved away from the historical practice of using traditional ROI based on the financial value of property protected by its flood projects (which tilted investment heavily towards high-income neighborhoods) to using a social-vulnerability index created by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which moves more funding to areas with the most at-risk populations.[8]
- In Raleigh, NC, the city explicitly measures environmental and social, as well as economic, outcomes of projects (the “triple bottom-line”) in its 2030 Comprehensive Plan.[9]
Use Change Management Best Practices to Build Support
Our most successful clients take a strategic approach to engaging internal and external stakeholders who are considered potential champions or detractors to implementation.
- For example, traditionally information is presented to community groups for comment and approval, but a fully equitable approach would be to engage the community up-front in a true dialogue to understand priorities, concerns, and opportunities for both sides while the program is still under design.
- Tools to consider include using steps from Dr. John Kotter’s Model[10], adapted and customized for more effective “place-based” or local use.
Conclusion: Importance of Investments in a More Equitable Future
Many municipalities currently face a myriad of deferred maintenance and equity imperatives – all of which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The path to reversing severe long-term under- and disinvestment must include large-scale, strategic capital program initiatives. Through engaging their communities, cities can address both historical disparities and identify investments that can build towards a more equitable future.
“The best time to plant a tree was 20 years ago, the second-best time is now.”
A common theme across the strategies documented here is the importance of change management to creating sustainable change. Whether starting from a top-down directive (e.g. executive order) or a bottom-up approach (e.g. employee-led, department level change), understanding the stakeholders involved and the relevant processes is critical to designing a more equitable approach. Another factor embedded in each of these strategies is the availability and monitoring of disaggregated data to ensure that all residents benefit from the changes implemented.
As equitable considerations take hold and begin to shift the balance of capital investment dollars to the previously neglected corners of the local map, municipalities should become better places to live, work, and enjoy for all residents. When combined with strong community engagement, data-driven project criteria, and thorough measurement and evaluation, funds that seemed too limited will deliver results above and beyond their scale. With the first American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) funds arriving to cities, states, and counties in the last month, and recent, additional infrastructure spending discussed at the federal level – now is the time to prepare stakeholders to rise and meet the moment.
[1] Zhao, Jerry Zhirong, et al. The Volcker Alliance, 2019, pp. 1–40, America’s Trillion-Dollar Repair Bill.
[2] Performance Measures, http://www.gfoa.org/materials/performance-measures.
[3] City of Seattle, Office of Planning & Community Development. Community Planning: Practice + Prioritization, pp. 4–32.
[4] Hackler, Darrene. Smart Incentives, 2021, pp. 1–5, Community Benefit Agreements: An Equitable Tool for Innovation District Development.
[5] Young, Harrison. “Austin Transit Partnership OKs Anti-Displacement Funding.” Austin Monitor, 18 Mar. 2021, http://www.austinmonitor.com/stories/2021/03/austin-transit-partnership-oks-anti-displacement-funding/.
[6] Philadelphia Energy Authority, “Solar Savings Grant Program.” https://solarizephilly.org/solar-savings-grant-program/
[7] Reach out Response Network, November 2020, pp. 1-91. Final Report on Alternative Crisis Response Models for Toronto.
[8] Wallace, Don. “A Climate Plan in Texas Focuses on Minorities. Not Everyone Likes It.” The New York Times, 24 July 2020, https://www.nytimes.com/2020/07/24/climate/houston-flooding-race.html.
[9] City of Raleigh, Office of City Planning. 2030 Comprehensive Plan – Update, pp. 123-124.
[10] “The 8-Step Process for Leading Change: Dr. John Kotter.” Kotter, 7 May 2021, http://www.kotterinc.com/8-steps-process-for-leading-change/.